Plastics are the most common materials used to produce all types of parts and finished products, ranging from simple consumer products to medical devices. Plastics are a very versatile class of materials, with thousands of possible polymer combinations, each with specific mechanical properties.
Manufacturing processes with plastics have been developed to cover a wide range of applications and part geometries. Any designer or engineer working in product development should be familiar with the manufacturing options available today, as well as new ones that presage future processes.
This guide presents all of the most common manufacturing processes for the production of plastic parts, as well as tips for choosing the right one for your application.
How to choose the right manufacturing process?
When selecting a manufacturing process, the following factors should be considered:
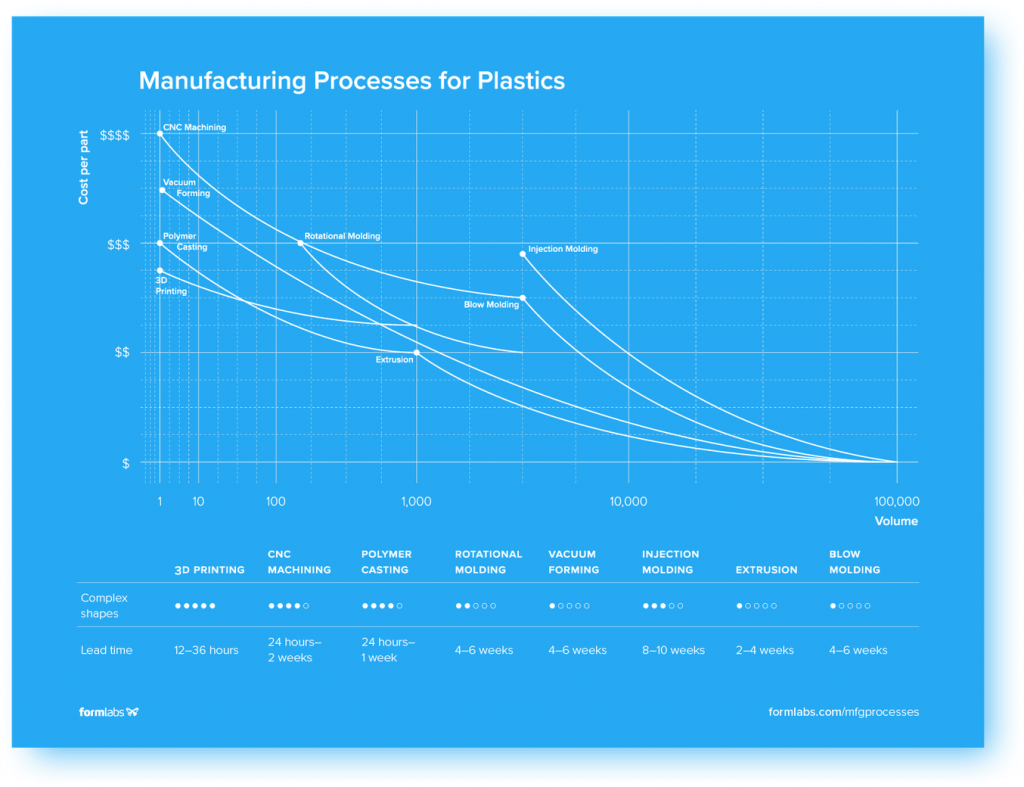
Part shape: Do parts have complex internal parts or require tight tolerances? Possible manufacturing options may be constrained by the part geometry. Design for manufacturing (DFM) optimization may also be required to make production more economical.
Volume/Price: What is the total or annual volume of parts you plan to manufacture? Some processes have high initial costs for tooling and set-up, but the cost per part produced is low. On the other hand, low-volume processes may have low start-up costs, but the cost per part remains constant or decreases marginally as the total volume increases, due to longer cycle times, less automation and more manual operations.
Turnaround time: How fast do you want your parts to be produced? Some processes can produce parts in 24 hours, others take months due to the tooling and set-up required for high volume production.
Types of plastics
Thousands of types of plastics are available with different base chemicals, additives and derivatives, formulated to have a wide range of functional and aesthetic properties.
To simplify the selection of the most suitable material for a given part or product, we will first look at the two main categories of plastics that exist: thermoplastics and thermosets.
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics are the most widely used. The main characteristic that differentiates them from thermoset plastics is that they can undergo numerous melting and hardening cycles without significant degradation of their properties. Thermoplastics are usually in the form of small granules or sheets, which are heated and shaped by various processes. The process is completely reversible because it does not involve chemical bonding, allowing for recycling or melting and reuse.
Common materials:
- Acrylic (PMMA)
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Polyamide (PA)
- Polylactic acid (PLA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)

Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.